Advanced Setup
The basic installations of the lab instance of the NFDI-MatWerk Data and Metadata repositories are accessible without SSL and the respective service must be addressed directly using the port number. Sometimes firewall settings do not allow for such usage without SSL. For addressing the services with “clean” URLs, e.g., if instead of https://my instance.mydomain.edu:8090/api/v1, a clean URL without the port number, like https://my instance.mydomain.edu/api/v1 is required, a web server in front of the two services which acts as a proxy needs to be set up. This web server can then also serve as an SSL endpoint and also be used with additional tools like the frontend collection as a web GUI.
Install Web Server and Create SSL Certificates
In this Documentation, Apache is taken as a web server and Let’s Encrypt is used to create SSL certificates. Thereafter, Apache is configured as a reverse proxy and at the end the frontend collection is installed for the web GUI.
A bwCloud instance based on Linux is used here to set up the server, as the hostname is pretty long, we just use e724fd14-XXXX-YYYY-ZZZZ-SOMETHING.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org as the hostname. You are free to choose whatevever instance for which you have admin rights. Remember to use the right hostname always. Please note that the following documentation provides the commands for linux systems which are most common while setting up remote servers. The commands need to be edited according to the operating system used.
Install Apache
Apache is required for “Let’s Encrypt”, and also for setting the reverse proxy for clean URLs. Follow the steps below to install Apache.
-
Enable ports 80 & 443 for public, based on the settings of your instance.
- Install Apache2 by using the following commands.
apt-get install apache2 systemctl status apache2.serviceThe output would then look like this:
[...] Active: active (running) since [...] - Set basic configuration of Apache2, by editing the file
000-default.conflocated in the directory/etc/apache2/sites-available/using a commandline editor like vim or nano. Comment the default ServerNamewww.example.comby putting a # in front of the corresponding line. Then add the hostname of the instance used. Here we use the hostnamee724fd14-XXXX-YYYY-ZZZZ-SOMETHING.ka.bw-cloud-instance.orgas mentioned previously.cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/ nano 000-default.conf #ServerName www.example.com ServerName e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org -
Save the file and exit the editor by typing Ctrl+O followed by enter and then Ctrl+X.
- Using the Apache command
a2ensiteenable the virtual host configuration file and start serving the website. Reload apache2 for the changes to take place.a2ensite 000-default.conf systemctl reload apache2
Now the default landing page becomes active and can be opened in your browser: http://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org. Note that the address starts with http instead of https. For https, an SSL certificate is needed, for which “Let’s Encrypt” can be used. How this is done is shown in the section below.
Create Certificate with Let’s Encrypt
- Execute the commands below to install necessary packages for Let’s Encrypt and to create an SSL certificate. When you run the
certbotcommand, Certbot will interactively guide you through the process of obtaining the certificate, configuring Apache to use the certificate, and setting up automatic renewal. Certbot will handle the communication with Let’s Encrypt’s servers to validate your domain ownership and issue the certificate.apt-get install certbot python3-certbot-apache apt-get install certbot python3-certbot-nginx certbot --apache -d e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.orgThe process looks like this:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): email@dot.org - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.3-September-21-2022.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server. Do you agree? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: y - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://e724fd14-3bfe-4f8d-93e8-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -After successful completion of setting up “Let’s Encrypt”, the following address can be reached or the old http address gets redirected to https: https://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org
- Create a folder called
templates, in which the root certificate from the “Let’s Encrypt” website is to be saved aslets-encrypt-r3.pem.mkdir templates cd templates/ curl https://letsencrypt.org/certs/lets-encrypt-r3.pem -o lets-encrypt-r3.pemAfter successful file transfer we get the following output:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 100 1826 100 1826 0 0 44536 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 44536 - Next import the downloaded certificate into the java keystore and check if key renewal works properly.
keytool -import -alias letsencryptauthorityx1 -cacerts -file lets-encrypt-r3.pemBy entering the default password, the certificate can be added to the keystore.
#default password is “changeit” Enter keystore password: Certificate was added to keystore -
Next check if the certificate renewal works properly by executing the following command. When you run
certbot renew --dry-run, Certbot will attempt to renew all the certificates that are near expiry, but it will not make any changes to the actual certificates or your server configuration. Instead, it will perform a series of tests to ensure that the renewal process would succeed under normal circumstances.certbot renew --dry-runThe output would look like this when the tests are successful:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org .conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Cert not due for renewal, but simulating renewal for dry run Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache Simulating renewal of an existing certificate fore724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - new certificate deployed with reload of apache server; fullchain is /etc/letsencrypt/live/ee724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org /fullchain.pem - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations, all simulated renewals succeeded: /etc/letsencrypt/live/e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org /fullchain.pem (success) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Create Dummy Landing Page
- For testing purposes, create a dummy landing page
index.htmlin the location var/www/matwerk using nano or any other commandline editor.cd /var/www/ mkdir matwerk cd matwerk/ nano index.html <html> <body> <h1> Hello MatWerk team-mate </h1> </body> </html> -
Save the file and exit the editor by typing Ctrl+O followed by enter and then Ctrl+X.
- Next, copy the contents of
000-default-le-ssl.confcontained in/etc/apache2/sites-available/tomatwerk-le-ssl.conf.cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/ cp 000-default-le-ssl.conf matwerk-le-ssl.conf - Now edit the
DocumentRootto/var/www/matwerkin the filematwerk-le-ssl.confusing nano or vim.nano matwerk-le-ssl.conf ... DocumentRoot /var/www/matwerk -
Save the file and exit the editor by typing Ctrl+O followed by enter and then Ctrl+X.
- Now disable the default old configuration file
000-default-le-ssl.confusing the Apache commanda2dissite.a2dissite 000-default-le-ssl.confOutput:
Site 000-default-le-ssl disabled. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl reload apache2 - Enable the new configuration file
matwerk-le-ssl.confusing the Apache commanda2ensite.a2ensite matwerk-le-ssl.confOutput:
Enabling site matwerk-le-ssl. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl reload apache2 - Reload Apache to activate the new configuration.
systemctl reload apache2 - The dummy landing page becomes now visible in the browser using the link: https://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/index.html
Create Reverseproxy Configuration
- For creating the reverseproxy configuration, add the following lines to the configuration file
matwerk-le-ssl.conf. First open it with a commandline editor like nano.nano matwerk-le-ssl.conf #Add these lines to your config ########################### SSLEngine on SSLProxyEngine On ProxyPreserveHost On ProxyPass /api/v1/schemas http://0.0.0.0:8040/api/v1/schemas ProxyPassReverse /api/v1/schemas http://0.0.0.0:8040/api/v1/schemas ProxyPass /api/v1/metadata http://0.0.0.0:8040/api/v1/metadata ProxyPassReverse /api/v1/metadata http://0.0.0.0:8040/api/v1/metadata ProxyPass /api/v1/ui http://0.0.0.0:8040/api/v1/ui ProxyPassReverse /api/v1/ui http://0.0.0.0:8040/api/v1/ui ProxyPass /api/v1/dataresources http://0.0.0.0:8090/api/v1/dataresources ProxyPassReverse /api/v1/dataresources http://0.0.0.0:8090/api/v1/dataresources ProxyPass /baserepo http://0.0.0.0:8090 ProxyPassReverse /baserepo http://0.0.0.0:8090 ##################### -
Save the file and exit the editor by typing Ctrl+O followed by enter and then Ctrl+X.
- Use the Apache command
a2enmodto enable theproxy_httpmodule.a2enmod proxy_httpOutput:
Considering dependency proxy for proxy_http: Enabling module proxy. Enabling module proxy_http. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl restart apache2 - Restart Apache to activate the new configuration.
systemctl restart apache2
Now the services (base-repo and MetaStore) can be accessed via Apache2, which also acts as an SSL endpoint. To test this, click the following link or copy and paste it in your browser: https://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/baserepo.
Note that that the port number 8090 for base-repo and 8040 for MetaStore are no longer needed.
The same can be tested using the command line interface (CLI) on your desktop:
curl https://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/baserepo
Output:
{
"_links" : {
"dataResources" : {
"href" : "http://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/dataResources{?page,size,sort}",
"templated" : true
},
"aMQPMessages" : {
"href" : "http:/e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/aMQPMessages{?page,size,sort}",
"templated" : true
},
"allIdentifierses" : {
"href" : "http://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/allIdentifierses{?page,size,sort}",
"templated" : true
},
"contentInformations" : {
"href" : "http://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/contentInformations{?page,size,sort}",
"templated" : true
},
"profile" : {
"href" : "http://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org/profile"
}
}
The services are now accessible via the REST-API through Apache. For better user experience, a GUI based access is also possible. For this, follow through the instructions in the next section.
Install Frontend-Collection
The frontend-collection is a set of generic web frontends for accessing RESTful services from the KIT Data Manager service portfolio. The idea is to have graphical user interfaces (GUI) available as a starting point without the need of developing own frontends.
- Change to super user to be able to install the
frontend collectionand change to the directorysoftwareand clone the frontend collection there, using git.su - matwerk cd software/ git clone https://github.com/kit-data-manager/frontend-collectionOutput:
Cloning into 'frontend-collection'... remote: Enumerating objects: 1987, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (363/363), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (169/169), done. remote: Total 1987 (delta 271), reused 256 (delta 194), pack-reused 1624 Receiving objects: 100% (1987/1987), 11.83 MiB | 14.05 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (1020/1020), done. - Check the contents of the newly cloned git repository
frontend-collectionusing thelscommand.ls frontend-collection/Output:
LICENSE images README.md index.html collection-management.html js css mapping-service-ui.html dashboard.html metadata-management.html definitions miserables.json elastic-search-base-repo.html repo-management.html elastic-search-fdo.html schema-management.html elastic-search-metastore.html test.html fdo-creator-ui.html typed-pid-maker-ui.html - Logout of super user and change to the directory
/var/www/matwerk/, and remove the dummy landing pageindex.htmlwhich was created earlier using thermcommand.logout cd /var/www/matwerk/ rm index.html - Now copy all the contents of the directory
frontend-collectionto the directory/var/www/matwerk/cp -r /home/matwerk/software/frontend-collection/* . - Now the web GUI based on the frontend collection becomes accessible at https://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org.
It would look similar to the picture below 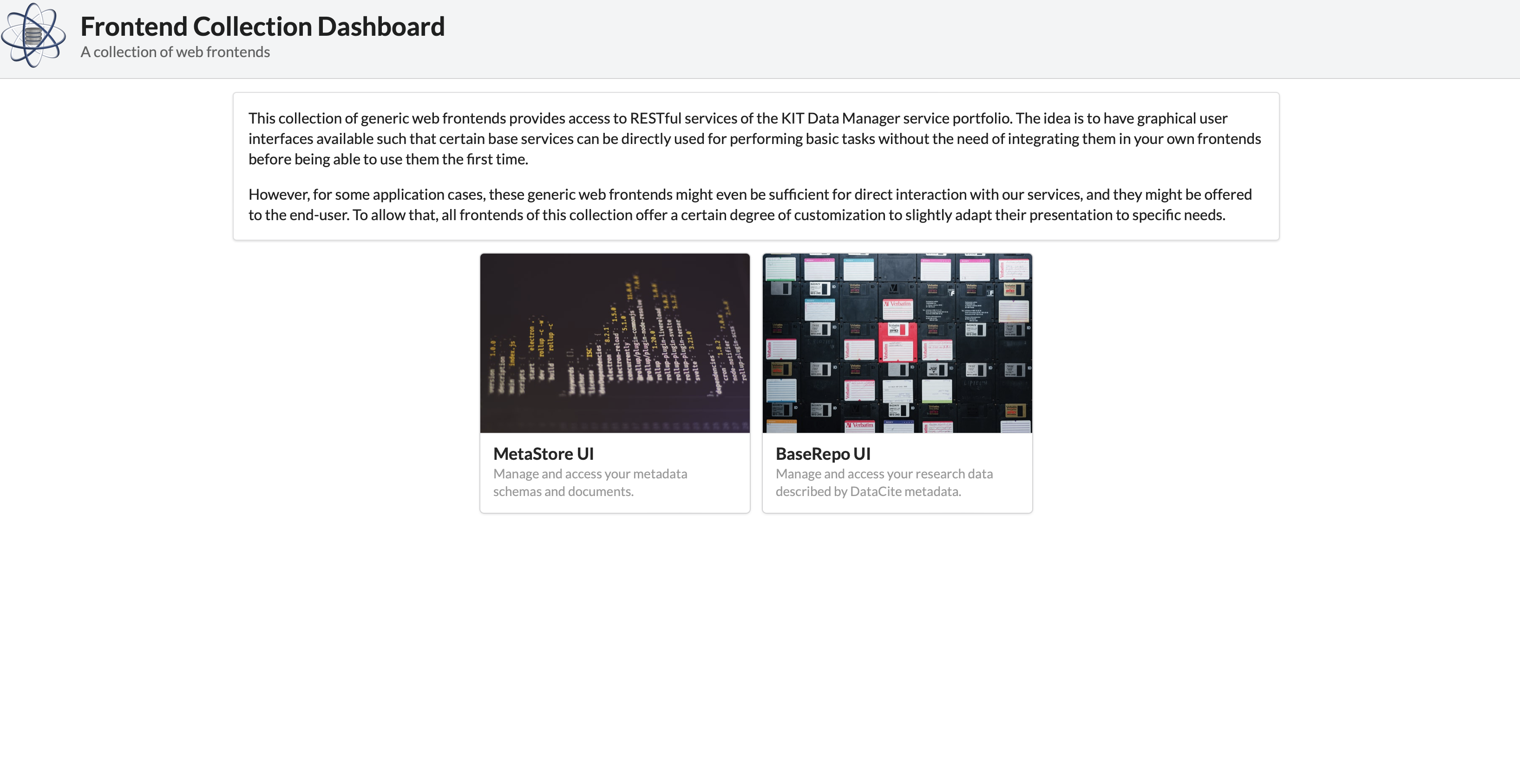
Note
To customize the dashboard, please refer to the documentation in the GitHub repository: https://github.com/kit-data-manager/frontend-collection/blob/main/README.md#basic-customization
If you have problems with ingesting data into the repositories, check the following parameter:
metastore.security.allowedOriginPattern=http*://e724fd14-xxx-yyy-zzz-ec995a17e8df.ka.bw-cloud-instance.org:*
#For Testing set it to
metastore.security.allowedOriginPattern=*